Microsoft Visual Studio is an environment which allows you to create, edit, save, debug, compile, and run C++ programs.
Projects Every C++ program is contained in its own project directory. Whenever you start a new homework assignment or any C++ program, you must create a project within Visual Studio first and add C++ source code files (text files with extension .cpp) to that project. In this handout, we will show you how.
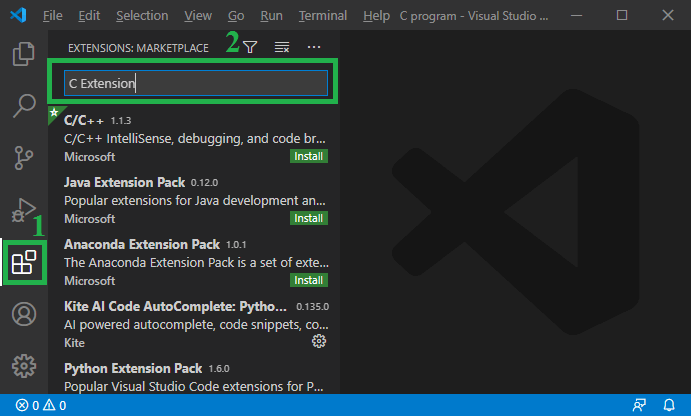
To create and run a C program using Visual Studio 2019 Once Visual Studio is started, click Z reate a new project. Select Empty Project and click Next. Enter an appropriate project name. A folder of the project name will be added under the repos folder. 1 Avoid using the built-in 'Run' button. Instead, open a new built-in terminal, activate your venv or conda environment and then execute your script via terminal.
Solutions A solution is a file that groups related C++ projects together in order to organize them. You will only need to create two solutions for this course: one for your homework projects and another for example projects given to you in PIC 10A.
To create your first project and solution for your homework, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open Microsoft Visual Studio by clicking the purple infinity icon
Select “Visual C++” from the drop-down menu. Then press “Start Visual Studio.”
Step 2: Select “Create a new project.”
Step 3: Under the “Language” drop down menu, select “C++” and then select “Empty Project” then the “Next” button.”
Step 4: Configure your new project. Under the “Project name:” enter the name of your project “Hw1”. If you are using your own computer, then one can leave the Location item as is. If you are using a Virtual PIC Lab machine, then under “Location:” enter the location where you want to save your project on the U drive, e.g. “U:”. Under “Solution name:” enter the name of your solution “Homework”. Then click the “Create” button.
Then your project will be ready to start:
Step 5: Your solution “Homework” and Project “Hw1” are displayed in the Solution Explorer. Right-click “Source files,” select “Add”, then “New Item” to create source code.
Step 6: Under Visual C++, select “Code.” Then select “C++” File in the middle frame. Enter the name of your C++ source code file “HelloWorld.cpp” and press “Add.” This will create the source code file (a plain text file) inside your Project1 Project folder and integrate it into your program.
Step 7: Type your C++ code into the source editor and press CTRL-S to save.

Step 8: After editing the source code file, select the “Build” menu and then “Build Hw1” to compile your project. The compiler will translate your source code into a binary executable (.exe) file written in your machine’s native language. The file “Hw1.exe” will be created as a result.
You will see the message “Build: 1 Succeeded” in the output window.
Step 9: To run program, select the Debug menu, followed by ”Start without debugging.”

Step 10: The output console will pop up and display the message “Hello World!”
Congratulations! You just completed your first C++ program!
You can find the solution (.sln) file in the solution directory “Z:Visual Studio ProjectsHomework”
You can find the source code HelloWorld.cpp in your Hw1 project subdirectory:
The object (.obj file) is located in your Project “Hw1” subfolder called “Debug.”
The standalone executable (.exe) file of your program is located in the “Debug” subfolder of your “Homework” solution folder.
This tutorial shows you how to write and run Hello World program in Java with Visual Studio Code. It also covers a few advanced features, which you can explore by reading other documents in this section.
For an overview of the features available for Java in VS Code, see Java Language Overview
If you run into any issues when following this tutorial, you can contact us by clicking the Report an issue button below.
Setting up VS Code for Java development
Coding Pack for Java
To help you set up quickly, you can install the Coding Pack for Java, which includes VS Code, the Java Development Kit (JDK), and essential Java extensions. The Coding Pack can be used as a clean installation, or to update or repair an existing development environment.
Install the Coding Pack for Java - macOS
Note: The Coding Pack for Java is only available for Windows and macOS. For other operating systems, you will need to manually install a JDK, VS Code, and Java extensions.
Installing extensions
If you are an existing VS Code user, you can also add Java support by installing Java Extension Pack, which includes these extensions:

The Java Extension Pack provides a Quick Start guide and tips for code editing and debugging. It also has a FAQ that answers some frequently asked questions. Use the command Java: Getting Started from the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)) to launch the guide.
You can also install extensions separately. The Extension Guide is provided to help you. You can launch the guide with the Java: Extension Guide command.
For this tutorial, the only required extensions are:
Settings for the JDK
Supported Java versions
The supported version for running the VS Code for Java extension and the supported version for your projects are two separate runtimes. To run VS Code for Java, Java SE 11 or above version is required; for projects, VS Code for Java supports projects with version 1.5 or above. For more details, refer to Configure JDK.
Using Java runtime configuration wizard
To help you configure correctly, we provide a runtime configuration wizard. You can launch the wizard by opening the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)) and typing the command Java: Configure Java Runtime, which will display the configuration user interface below.
Note: To configure multiple JDKs, see Configure JDK. To enable Java preview features, see How can I use VS Code with new Java versions
Using VS Code settings

How To Execute Code In Visual Studio
Alternatively, you can configure JDK settings using the VS Code Settings editor. A common way to do this is setting the value of the JAVA_HOME system environment variable to the install location of the JDK, for example, C:Program FilesJavajdk-13.0.2. Or if you want to configure only VS Code to use the JDK, use the java.home setting in VS Code's User or Workspace settings.
Installing a Java Development Kit (JDK)
When you need install a JDK, we recommend you to consider installing from one of these sources:
Creating a source code file
Create a folder for your Java program and open the folder with VS Code. Then in VS Code, create a new file and save it with the name Hello.java. When you open that file, the Java Language Server automatically starts loading, and you should see a loading icon on the right side of the Status Bar. After it finishes loading, you will see a thumbs-up icon.
Note: If you open a Java file in VS Code without opening its folder, the Java Language Server might not work properly.
VS Code will also try to figure out the correct package for the new type and fill the new file from a template. See Create new file.
You can also create a Java project using the Java: Create Java Project command. Bring up the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)) and then type java to search for this command. After selecting the command, you will be prompted for the location and name of the project. You can also choose your build tool from this command.
Visual Studio Code also supports more complex Java projects, see Project Management.
Editing source code
You can use code snippets to scaffold your classes and methods. VS Code also provides IntelliSense for code completion, and various refactor methods.
To learn more about editing Java, see Java Editing.
Running and debugging your program
To run and debug Java code, set a breakpoint, then either press F5 on your keyboard or use the Run > Start Debugging menu item. You can also use the Run|Debug CodeLens options in the editor. After the code compiles, you can see all your variables and threads in the Run view.
The debugger also supports advanced features such as Hot Code replacement and conditional breakpoints.
For more information, see Java Debugging.
More features
Run Code On Visual Studio
The editor also has much more capability for your Java workload.
Visual Studio Free Version
- Editing Java explains how to navigate and edit Java in more details
- Debugging illustrates all the key features of the Java Debugger
- Testing provides comprehensive support for JUnit and TestNG framework
- Java Project Management shows you how to use a project view and work with Maven
- Spring Boot and Tomcat and Jetty demonstrate great framework support
- Java Web Apps shows how to work with Java Web App in VS Code
