JavaScript is one of the most popular programming languages for web programming. “JavaScript Cheat Sheet — Basic ES6 Syntax and Methods” is published by John Au-Yeung in JavaScript in Plain English. JavaScript cheat Sheet Javascript ES6 Cheatsheet - the best of JS ES6. JavaScript Best Practices and Coding Conventions - Write Clean Code; JavaScript object cheatsheet; Creating a CheatSheet Template using HTML, CSS & JavaScript; Regular Expressions (RegEx) in 100 Seconds; Top Eight JavaScript Objects And Array Functions You Should Know! This page provides an overall cheat sheet of all the capabilities of RegExp syntax by aggregating the content of the articles in the RegExp guide. If you need more information on a specific topic, please follow the link on the corresponding heading to access the full article or head to the guide.
- Javascript Es6 Cheat Sheet Pdf
- Javascript Es6 Cheat Sheet
- Javascript Es6 Cheat Sheet Pdf
- Javascript Es6 Cheat Sheet
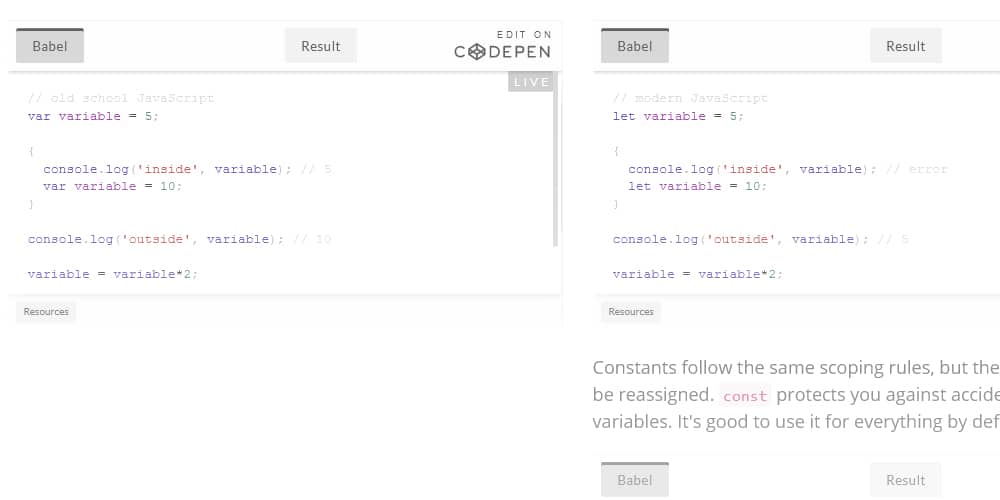
Functional programming is a style that treats computation as the evaluation ofmathematical functions and avoids changing-state and mutable data.
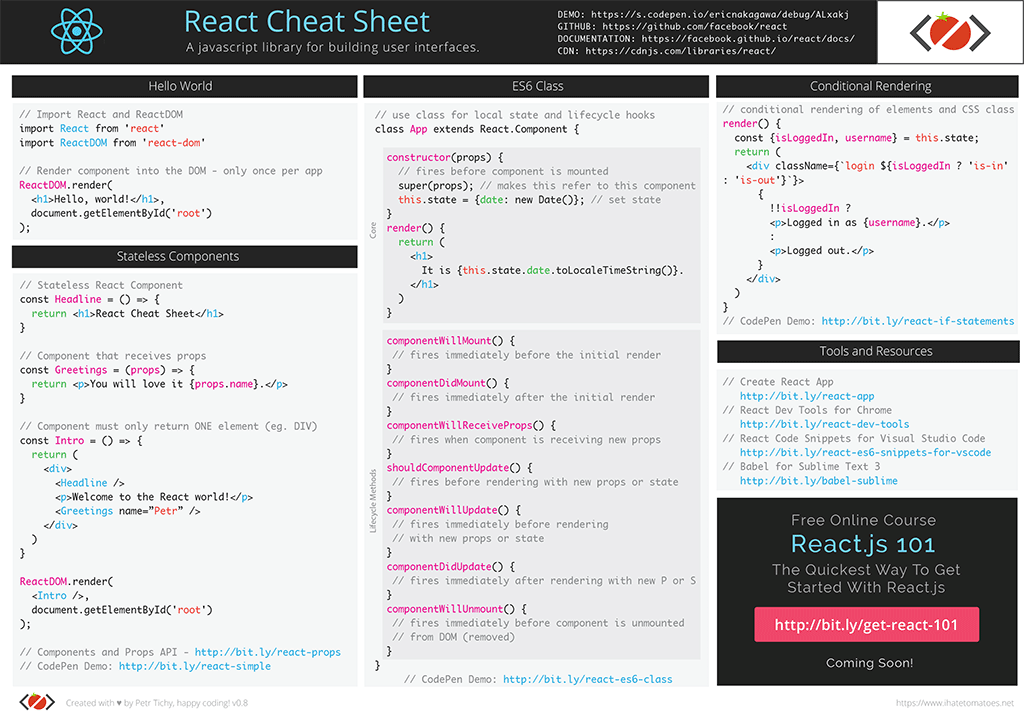
Arrow Functions (Fat Arrows)
Arrow functions create a concise expression that encapsulates a small piece of functionality. Additionally,arrows retain the scope of the caller inside the function eliminating the need of self = this.
Example
Read more at MDN Arrow_functions
Function Delegates
Function delegates encapsulate a method allowing functions to be composed or passed as data.
Example
Expressions Instead of Statements
Statements define an action and are executed for their side effect. Expressions produce a result without mutating state.
Statement (bad)
Expression (good)
Higher Order Functions
A function that accepts another function as a parameter, or returns another function.
Example
Currying
Currying allows a function with multiple arguments to be translated into a sequence of functions. Curried functions can be tailored to match the signature of another function.
Example
Array Manipulation Functions
Array Functions are the gateway to functional programming in JavaScript. These functions make short work of most imperative programming routines that work on arrays and collections.
[].every(fn)Checks if all elements in an array pass a test.
[].some(fn) | [].includes(fn)Checks if any of the elements in an array pass a test.
[].find(fn)Returns the value of the first element in the array that passes a test.
[].filter(fn)Creates an array filled with only the array elements that pass a test.
[].map(fn)Creates a new array with the results of a function applied to every element in the array.
Javascript Es6 Cheat Sheet Pdf
[].reduce(fn(accumulator, currentValue))Executes a provided function for each value of the array (from left-to-right). Returns a single value, the accumulator.
[].sort(fn(a,b)) warning, mutates state!Modifies an array by sorting the items within an array. An optional compare function can be used to customize sortbehavior.
Javascript Es6 Cheat Sheet
[...arr].sort()Use the spread operator to avoid mutation.
[].reverse() warning, mutates state!Reverses the order of the elements in an array. Use the spread operator to avoid mutation. [...arr].reverse()
Few useful librariries for Data Manipulation:
Javascript Es6 Cheat Sheet Pdf
Method Chaining
Method chains allow a series of functions to operate in succession to reach a final result. Method chains allow function composition similar to a pipeline.
Javascript Es6 Cheat Sheet

Example
Pipelines
A pipeline allows for easy function composition when performing multiple operations on a variable. Since JavaScript lacks a Pipeline operator, a design pattern can be used to accomplish the task.
Example
Like us to show some Love:
